
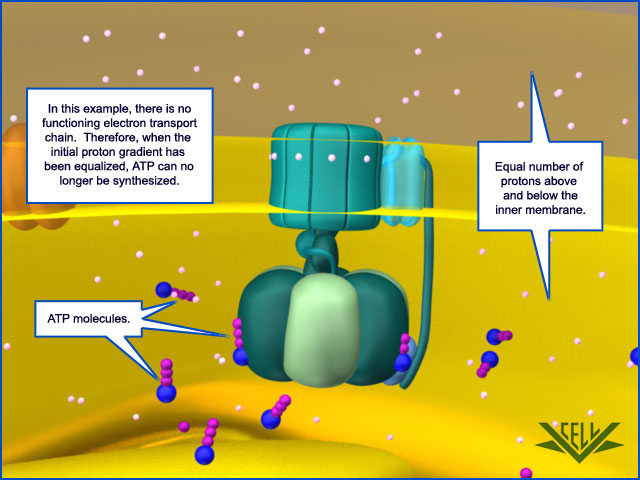
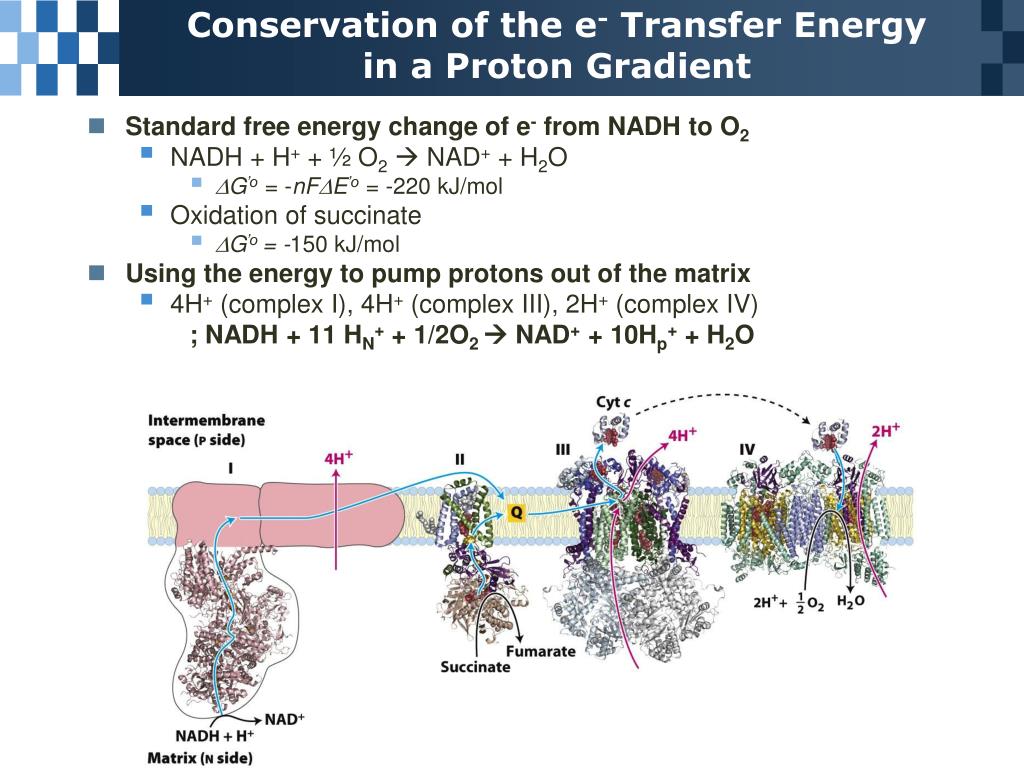
The flow of protons back into the matrix of the mitochondrion via ATP synthase provides enough energy for ADP to combine with inorganic phosphate to form ATP. The protons move back across the inner membrane through the enzyme ATP synthase. The energy of the oxygen, the terminal acceptor in the ETC, is used to pump protons from the matrix into the intermembrane space, storing energy in the form of a transmembrane electrochemical gradient. The carriers pass electrons to the electron transport chain (ETC) in the inner mitochondrial membrane, which in turn pass them to other proteins in the ETC. The oxidation of acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) in the mitochondrial matrix is coupled to the reduction of a carrier molecule such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). Molecules such as glucose are metabolized to produce acetyl CoA as a fairly energy-rich intermediate. Oxidative phosphorylation involves two processes - the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis - and occurs in mitochondria. In brief, the hypothesis was that most adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthesis in respiring cells comes from the electrochemical gradient across the inner membranes of mitochondria by using the energy of NADH and FADH 2 formed during the oxidative breakdown of energy-rich molecules such as glucose. Mitchell proposed the chemiosmotic hypothesis in 1961. The stored energy is used to photophosphorylate ADP, making ATP, as protons move through ATP synthase. For instance, in chloroplasts during photosynthesis, an electron transport chain pumps H + ions (protons) in the stroma (fluid) through the thylakoid membrane to the thylakoid spaces. The generation of ATP by chemiosmosis occurs in mitochondria and chloroplasts, as well as in most bacteria and archaea.
PROTON GRADIENT FREE
It allows protons to pass through the membrane and uses the free energy difference to phosphorylate adenosine diphosphate (ADP), making ATP. This process is related to osmosis, the movement of water across a selective membrane, which is why it is called "chemiosmosis".ĪTP synthase is the enzyme that makes ATP by chemiosmosis. Hydrogen ions, or protons, will diffuse from a region of high proton concentration to a region of lower proton concentration, and an electrochemical concentration gradient of protons across a membrane can be harnessed to make ATP. An ion gradient has potential energy and can be used to power chemical reactions when the ions pass through a channel (red).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
